"Microplastics: A Threat To Our Oceans And Wildlife"
Editor's note: "Microplastics: A Threat To Our Oceans And Wildlife" has published today date. This topic is very important for us to read because "Microplastics: A Threat To Our Oceans And Wildlife".
We put together this Microplastics: A Threat To Our Oceans And Wildlife guide to help target audience make the right decision.
| Key Topic | Description |
| Topic A |
|
| Topic B |
|
| Topic C |
|
FAQ
Microplastics are tiny pieces of plastic that can have detrimental effects on our oceans and wildlife. They can be ingested by organisms, accumulate in the food chain, and even enter the human body. Understanding microplastics and their impact is crucial for protecting our marine environment. This FAQ addresses common questions and concerns about microplastics.

10 of the most dangerous plastics polluting our oceans - Source www.marineconservation.org.au
Question 1: What are microplastics and where do they come from?
Microplastics are small plastic particles that are less than 5 millimeters in size. They can originate from various sources, including the breakdown of larger plastic items, synthetic materials in personal care products, and industrial processes. Microplastics can be found in both freshwater and marine environments.
Question 2: What are the impacts of microplastics on wildlife?
Microplastics can have a range of negative effects on wildlife. Ingestion of microplastics can cause physical blockages in the digestive tract, leading to starvation. They can also leach toxic chemicals into the bloodstream, disrupting hormone balance and reproductive functions. Microplastics can entangle animals, restrict movement, and impair their ability to feed.
Question 3: Are microplastics present in the human food chain?
Yes, microplastics have been found in various seafood species, including shellfish, fish, and marine mammals. When consumed by humans, these microplastics can accumulate in the body and potentially pose health risks. Research is ongoing to determine the long-term effects of microplastic ingestion on human health.
Question 4: What are we doing to address the microplastic issue?
Addressing the microplastic issue involves a multifaceted approach. Efforts are underway to reduce plastic consumption, improve waste management practices, and develop biodegradable alternatives to plastic products. Research and innovation play a vital role in understanding the sources, impacts, and potential solutions for microplastic pollution.
Question 5: What can I do to help reduce microplastic pollution?
There are several ways individuals can contribute to reducing microplastic pollution. Reducing single-use plastics, recycling properly, and supporting sustainable businesses are practical steps. Additionally, raising awareness and advocating for policy changes that promote responsible plastic use are crucial.
Question 6: What does the future hold for microplastics?
The long-term implications of microplastic pollution are still being investigated. Ongoing research and technological advancements will provide valuable insights into the potential risks and solutions. Collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and the general public is essential for effectively addressing this emerging environmental challenge.
Understanding the nature, impacts, and mitigation strategies for microplastics is crucial for safeguarding the health of our oceans and wildlife. Through collective action and continued research, we can work towards a sustainable future where microplastic pollution is minimized.
Stay tuned for our next article, which will delve deeper into the scientific research on microplastics and their effects on marine ecosystems.
Tips
Microplastics are a growing threat to our oceans and wildlife. These tiny pieces of plastic, less than 5mm in size, can be ingested by marine animals, leading to health problems and even death. They can also accumulate in the food chain, posing a risk to human health. In order to protect our oceans and wildlife, we need to take action to reduce our use of plastic and prevent it from entering the environment.
Here are six tips to help you reduce your plastic footprint:
Tip 1: Microplastics: A Threat To Our Oceans And Wildlife Choose reusable items over single-use plastics. This includes items like water bottles, coffee cups, and shopping bags. There are many affordable and stylish reusable options available.
Tip 2: Avoid products that contain microplastics. These products include many types of cosmetics, toothpaste, and cleaning products. Look for products that are labeled as "microplastic-free" or "biodegradable."
Tip 3: Properly dispose of plastic waste. Never litter plastic, and make sure to recycle it when possible. Recycling helps to reduce the amount of plastic that ends up in our oceans.
Tip 4: Support businesses that are taking action to reduce their plastic use. This includes businesses that use sustainable packaging, offer reusable products, and recycle their waste.
Tip 5: Educate yourself and others about the dangers of microplastics. The more people who are aware of this issue, the more likely we are to take action to address it.
Tip 6: Get involved in your community. There are many ways to get involved in efforts to reduce plastic pollution. You can volunteer your time, donate to organizations that are working on this issue, or simply spread the word about the dangers of microplastics.
By following these tips, you can help to reduce your plastic footprint and protect our oceans and wildlife.
Microplastics: A Threat To Our Oceans And Wildlife
Microplastics pose a grave threat to our oceans and wildlife. These tiny particles, less than 5 mm in size, accumulate in marine environments, causing widespread harm to marine ecosystems. Six key aspects highlight the severity of this issue:
- Ingestion: Microplastics are ingested by marine organisms, causing digestive issues and malnutrition.
- Entanglement: Plastic debris entangles animals, hindering their movement, feeding, and survival.
- Toxic Effects: Microplastics contain harmful chemicals that leach into marine organisms, impairing their health.
- Habitat Degradation: Microplastics alter marine habitats, reducing biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
- Biomagnification: Microplastics accumulate in the food chain, becoming more concentrated in higher trophic levels.
- Human Health: Microplastics can enter the human food chain through seafood consumption, posing potential health risks.
These interconnected aspects demonstrate the urgent need to address the microplastics crisis. Ingestion and entanglement directly harm individual organisms, while toxic effects and habitat degradation impact entire ecosystems. Biomagnification and human health concerns highlight the far-reaching consequences of microplastic pollution. Protecting our oceans and wildlife requires reducing single-use plastics, promoting recycling, and developing innovative solutions to mitigate this pervasive threat.
Impact of microplastics on wildlife - Wasser 3.0 - Source wasserdreinull.de
Microplastics: A Threat To Our Oceans And Wildlife
Microplastics are tiny pieces of plastic that are less than 5 millimeters in length. They can come from a variety of sources, including plastic bags, bottles, and clothing. Microplastics are a threat to our oceans and wildlife because they can be ingested by marine animals, which can lead to a number of health problems. Microplastics can also absorb toxins from the water, which can then be passed up the food chain.

Microplastics: An Invisible Threat to Our Oceans - KOL Social Magazine - Source thekolsocial.com
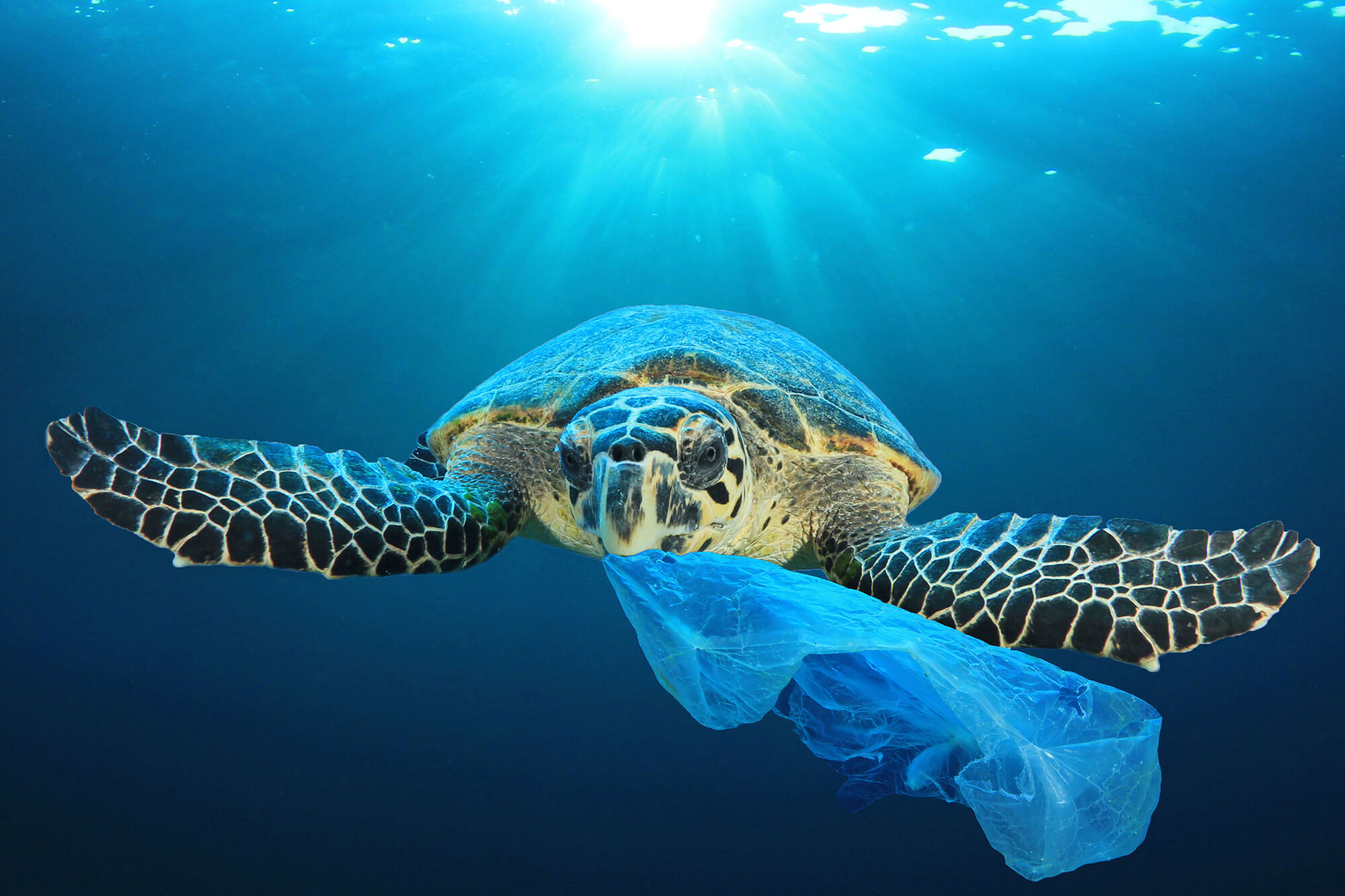
One of the most well-known impacts of microplastics on marine wildlife is the ingestion of plastic by sea turtles. Sea turtles often mistake plastic bags for jellyfish, which are a common part of their diet. When sea turtles eat plastic bags, they can become injured or even die. Microplastics can also be ingested by other marine animals, such as fish, birds, and whales. The ingestion of microplastics can lead to a number of health problems, including starvation, malnutrition, and reproductive problems.
In addition to the ingestion of plastic, microplastics can also absorb toxins from the water. These toxins can then be passed up the food chain, where they can have a negative impact on human health. For example, microplastics have been found to contain toxins that can cause cancer, reproductive problems, and developmental disorders.
Microplastics are a serious threat to our oceans and wildlife. It is important to take steps to reduce the amount of plastic pollution in our oceans. We can do this by reducing our use of plastic products, recycling plastic whenever possible, and properly disposing of plastic waste.
Table: Impacts of Microplastics on Marine Wildlife
| Impact | Example |
|---|---|
| Ingestion | Sea turtles often mistake plastic bags for jellyfish, which are a common part of their diet. When sea turtles eat plastic bags, they can become injured or even die. |
| Absorption of toxins | Microplastics can absorb toxins from the water, which can then be passed up the food chain. These toxins can have a negative impact on human health. |
| Physical damage | Microplastics can cause physical damage to marine animals, such as lacerations and blockages. |
Conclusion
Microplastics are a serious threat to our oceans and wildlife. They can be ingested by marine animals, which can lead to a number of health problems. Microplastics can also absorb toxins from the water, which can then be passed up the food chain. It is important to take steps to reduce the amount of plastic pollution in our oceans. We can do this by reducing our use of plastic products, recycling plastic whenever possible, and properly disposing of plastic waste.
The problem of microplastics is a complex one, but it is one that we must address. By working together, we can reduce the amount of plastic pollution in our oceans and protect our marine wildlife.